Abstract
Large scale molecular profiling studies in AML patients have suggested that stepwise acquisition of somatic mutations is crucial in driving leukemic development. High variant allele frequency (VAF) mutations in epigenetic modifier genes, such as TET2 and IDH1/2, are thought to occur early in AML pathogenesis while oncogenic mutations with typically lower VAF mutations, including FLT3 and NRAS, are suggested to occur late in disease evolution. While bulk DNA sequencing has catalogued co-mutations found in individual AMLs, it cannot unveil the heterogeneity and composition of clones that makes up the disease. Elucidating the architecture and clone-specific molecular profiles at the single cell resolution will be key to understanding how sequential and/or parallel mutation acquisition drives myeloid transformation.
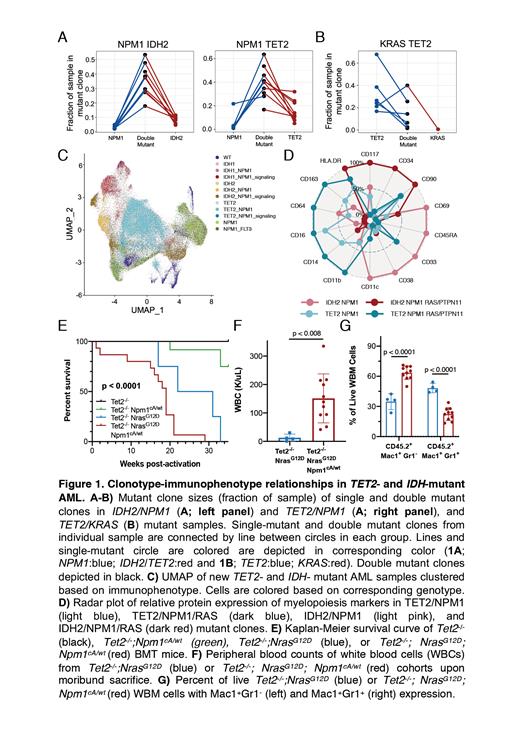
To assess the clonal architecture of AML, we previously performed single cell DNA sequencing (scDNA seq) in 146 patients with myeloid malignancies. We have further identified specific mutational combinations driving clonal expansion in TET2- or IDH1/2- mutant AML samples. These studies suggest TET2 and IDH1/2 can cooperate to promote clonal expansion with DNMT3A and NPM1 (Figure 1A). However, TET2 or IDH1/2 mutant clones that acquired KRAS mutations underwent minimal clonal expansion, suggesting mutant-pair specific fitness alterations (Figure 1B). To further identify how co-mutational pairing impacted clonal fitness and differentiation, we integrated the scDNA platform with immunophenotypic profiling of 45 cell surface markers and analyzed new TET2- and IDH1/2- mutant AML samples (Figure 1C). We identified clone-specific differences in lineage markers depending on co-mutational partners. NPM1 co-mutant clones were enriched for more primitive markers (CD33), whereas NRAS co-mutant clones possessed high expression of myeloid differentiation markers (CD14/CD11b), suggestive of clone-specific fitness landscapes across hematopoietic differentiation. We also identified divergent clonotype-immunophenotype patterns in TET2- and IDH2-mutant clones harboring NPM1/RAS mutations, suggesting that initiating mutations may prime mutant clones for very different evolutionary trajectories as they acquire similar mutations in leukemogenesis (Figure 1D).
To deterministically delineate the relationship between clonal evolution and myeloid transformation, we generated Cre-inducible single (Tet2 -/-), double (Tet2 -/-/Nras G12Dand Tet2 -/-/Npm1 cA/wt), and triple (Tet2 -/-/Npm1 cA/wt/Nras G12D) mutant mice and evaluated differences in chimerism, immunophenotype, and survival. We observed a shortened survival for double and triple mutant mice, compared to Tet2 -/- only mice (Figure 1E). As previously reported, Tet2 -/-/Nras G12D mice developed a CMML-like phenotype. Critically, the addition of Npm1 resulted in a more rapid disease onset and transformation to AML (Figure 1F). Moreover, triple mutant WBM transplanted to form a fully penetrant disease into secondary recipients, while double mutant Tet2 -/-/Nras G12D WBM failed to form disease within 3 months of transplant, suggesting a difference in the cell population responsible for disease propagation. Immunophenotypic alterations were evident with Tet2 -/-/ Nras G12D displaying an increase in Mac1 +Gr1 + cells compared to Tet2 -/-/Npm1 cA/wt/Nras G12D mice which possessed increased Mac1 +Gr1 - cells and expansion of lineage negative cells (Figure 1G). These findings align with the clonotype specific expression patterns observed in clinical specimen and suggest that myeloid transformation and maturation biases are influenced by specific mutational combinations.
Miles: Mission Bio: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Bowman: Mission Bio: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Carroll: Janssen Pharmaceutical: Consultancy; Incyte Pharmaceuticals: Research Funding. Levine: Astellas: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Auron: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Honoraria; QIAGEN: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Mission Bio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Isoplexis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Celgene: Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy; Imago: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; Prelude: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Ajax: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Zentalis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Honoraria; C4 Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Lilly: Honoraria; Morphosys: Consultancy.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal